
LEARJET 35 COCKPIT INSTRUMENTS
Airspeed Indicator
An Airspeed Gauge or better known as an Airspeed Indicator is used by pilots during all forms of flight. This is because the indicator provides the aircraft's airspeed which act as guidance to maintain the airspeed.

Markings on Airspeed Indicator
The use of color-coded markings on the Indicator has definitely improved the overall aspects of the aircraft. These marking located on the outer surface of the Indicator consists of several coloured lines and arcs, which has been effective in describing the aircraft’s speed.

Airspeed Terminology
GS = Ground Speed
WS = Wind Speed
CAS = Calibrated Airspeed
EAS = Equivalent Airspeed
Ground speed is basically the speed of the aircraft relative to the ground while wind speed is caused by air moving from high pressure to low pressure.
Airspeed is calculated by taking into consideration 2 factors, ground speed and wind speed.

Equal Airspeed
Both aircraft have the same airspeed (160 mph). The top aircraft flies with the 40 mph wind, so its ground speed is 200 mph. (Airpseed = Ground Speed - Wind Speed; 160 = 200 - 40 ). The lower aircraft flies into the 40 mph wind, so its ground speed is only 120 mph. (160 = 120 - (-40) ).
Equal Wind speed
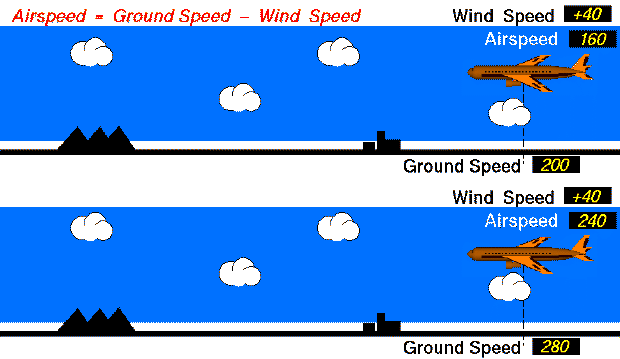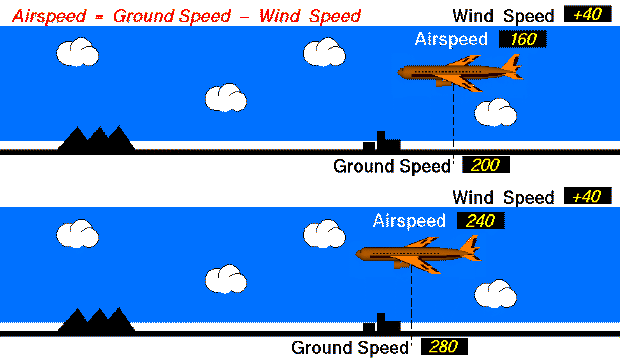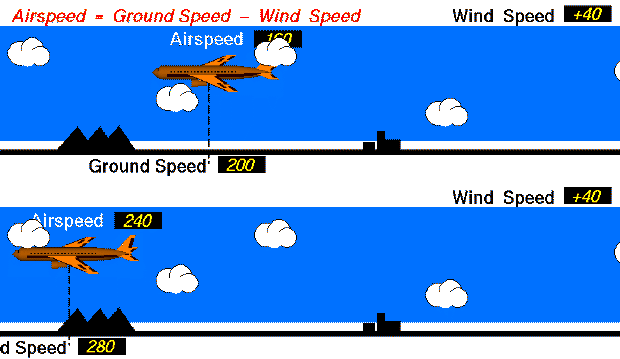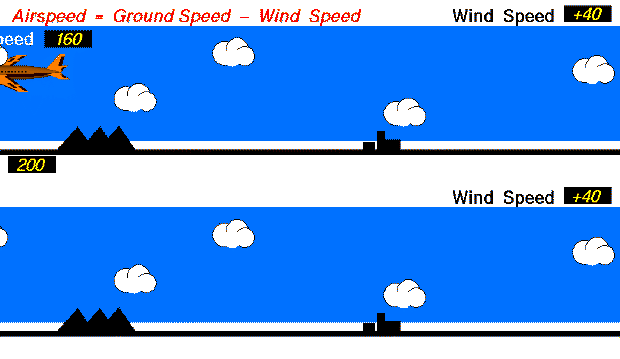
Both aircraft have the same wind speed (40 mph). The top aircraft flies with an airspeed of 160 mph , so its ground speed is 200 mph. (Airpseed = Ground Speed - Wind Speed; 160 = 200 - 40 ). The lower aircraft flies with an airspeed of 240 mph, so its ground speed is 280 mph. (240 = 280 - 40 ).
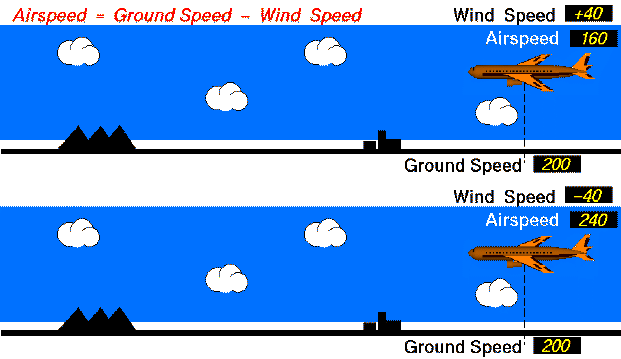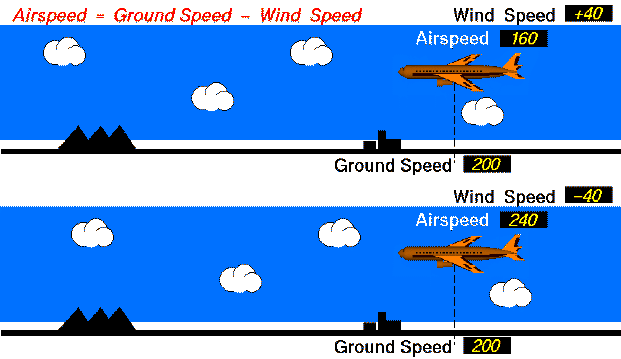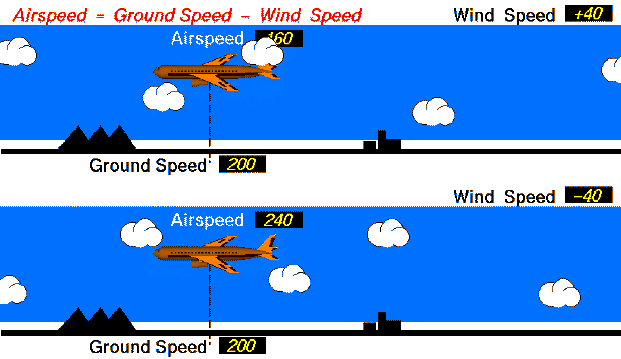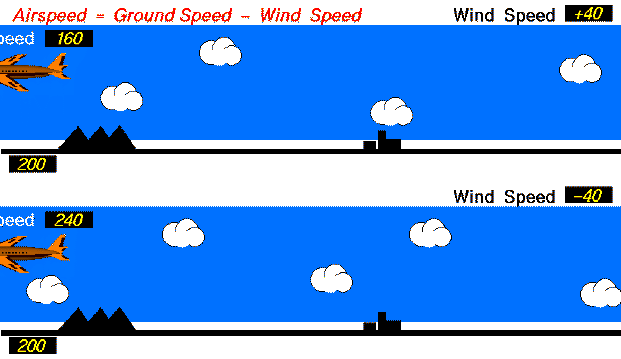
Equal Ground speed
Both aircraft have the same ground speed (200 mph). The top aircraft flies with the 40 mph wind, so its airspeed is 160 mph. (Airpseed = Ground Speed - Wind Speed; 160 = 200 - 40 ). The lower aircraft flies into the 40 mph wind, so its airspeed is 240 mph. (240 = 200 - (-40) ).